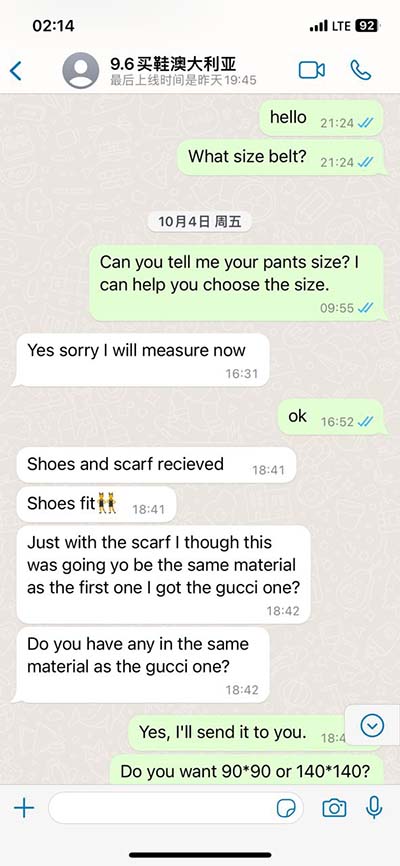
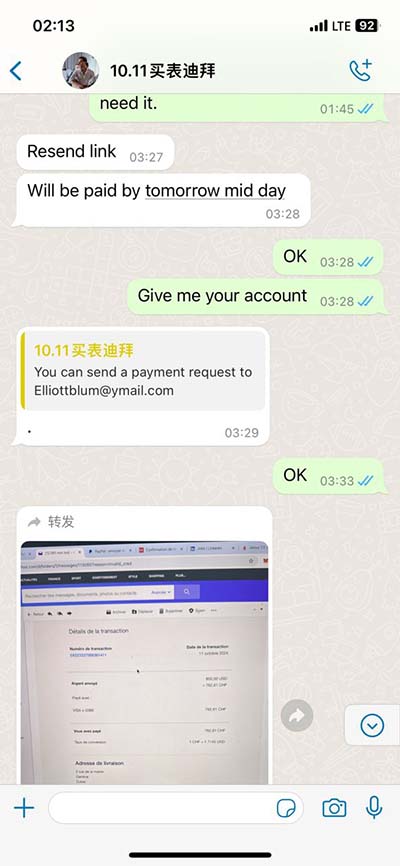
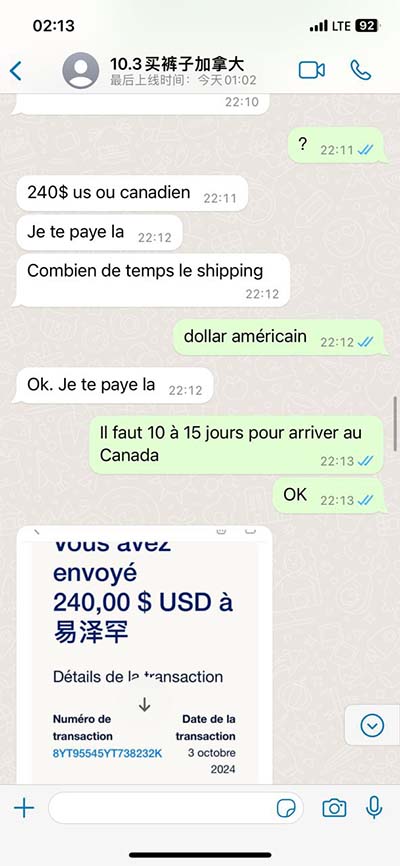
lv gv cv pv | Ventricular Pressure lv gv cv pv Ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops are an excellent tool for visualizing changes in ventricular function in response to changes in preload, afterload and inotropy.
FedEx izmanto sīkdatnes. Šajā vietnē tiek izmantotas sīkdatnes un līdzīgas tehnoloģijas (turpmāk kopā — sīkdatnes). Mēs izmantojam funkcionālās, analītiskās un izsekošanas sīkdatnes. Ja vēlaties saņemt papildu informāciju par sīkdatnēm, ko izmantojam, noklikšķiniet šeit. Jūsu piekrišana mums nav nepieciešama, lai .
0 · Ventricular pressure
1 · Ventricular Pressure
2 · CV Physiology
Firmas.lv - informācija biznesa lēmumu pieņemšanai. No 1992.gada līdz šodienai: LR Uzņēmumu reģistra juridiskā un ZL.lv faktiskā informācija. . Rīga, Festivāla iela 10. Atrasti 1 uzņēmumi, tai skaitā MILN GROUP, SIA un citi. Zemesgrāmatas izziņa (Paraugs) . Festivāla iela 10, Rīga, LV-1057 .
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against .Interdependent Effects of Preload, Afterload and Inotropy on Ventricular Pressure-Volume .
Ventricular pressure
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. .
A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop .
Interdependent Effects of Preload, Afterload and Inotropy on Ventricular Pressure-Volume Loops. In the intact organism, changes in preload, afterload and inotropy are interdependent, meaning . Ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops are an excellent tool for visualizing changes in ventricular function in response to changes in preload, afterload and inotropy.We have used many valves with the nomenclature of FV, PV, HV, XV, etc without knowing the actual function and description of their abbreviated names. In this article we will learn about: .Real-time left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real .
Right heart contractility is partially dependent on coordinated contraction with the LV (particularly the septum), and therefore is decreased with LV systolic failure or conducting .This review focuses on the fundamentals of left ventricular (LV) PV analysis highlighting practical aspects of PV measurements, interpretation of signals and potential applications to clinical . Introduction: The left ventricle (LV) pressure-volume loop (PV-loop) is a powerful tool for evaluating LV function. Current non-invasive cardiac MRI-based methods for . A recently published study applying RV PV analysis to LVAD recipients demonstrated that even patients with echocardiographically normal appearing RVs had only .
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. .
A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop .Interdependent Effects of Preload, Afterload and Inotropy on Ventricular Pressure-Volume Loops. In the intact organism, changes in preload, afterload and inotropy are interdependent, meaning . Ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops are an excellent tool for visualizing changes in ventricular function in response to changes in preload, afterload and inotropy.
We have used many valves with the nomenclature of FV, PV, HV, XV, etc without knowing the actual function and description of their abbreviated names. In this article we will learn about: .
Real-time left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real . Right heart contractility is partially dependent on coordinated contraction with the LV (particularly the septum), and therefore is decreased with LV systolic failure or conducting .This review focuses on the fundamentals of left ventricular (LV) PV analysis highlighting practical aspects of PV measurements, interpretation of signals and potential applications to clinical .
Ventricular Pressure
CV Physiology
Introduction: The left ventricle (LV) pressure-volume loop (PV-loop) is a powerful tool for evaluating LV function. Current non-invasive cardiac MRI-based methods for .
The Be All End All Guide to the "fastest way to level 80". Currently my "record" (I haven't tried this in a speed run fashion, but I have done it 5-6 times) is ~14 hours from 0-80. From my experience, the fastest way of .
lv gv cv pv|Ventricular Pressure